
Sickle hemoglobin polymerization causes a host of secondary molecular and cellular changes, many of which impair blood flow and contribute to tissue damage. Sickle hemoglobin forms rod-like polymers in deoxygenated red cells in areas of the circulation, with low oxygen tension, acidosis, or hyperosmolarity. Sickle cell disease is often called “the first molecular disease” because the biochemical alteration in sickle hemoglobin described by Linus Pauling in 1948 was one of the first lesions identified at the molecular level for a human disease. It is a genetic disorder with an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. It is common in individuals of African, Caribbean, Mediterranean, Arab, and other Middle Eastern descent. Sickle cell disease is a highly prevalent disease in the United States, affecting 1 in 500 African American infants.


Baseline hemodynamic and laboratory values in patients with sickle cell disease can be confused with sepsis.Sickle cell disease causes a chronic hemolytic anemia associated with acute and chronic vaso-occlusion.In addition, serologic barriers pose enduring roadblocks to the optimization of transfusion therapy for patients with SCD, and the syndrome of massive hemolytic transfusion reactions and hyperhemolysis in SCD persists as a life-threatening complication for which appropriate clinical management is not yet defined.
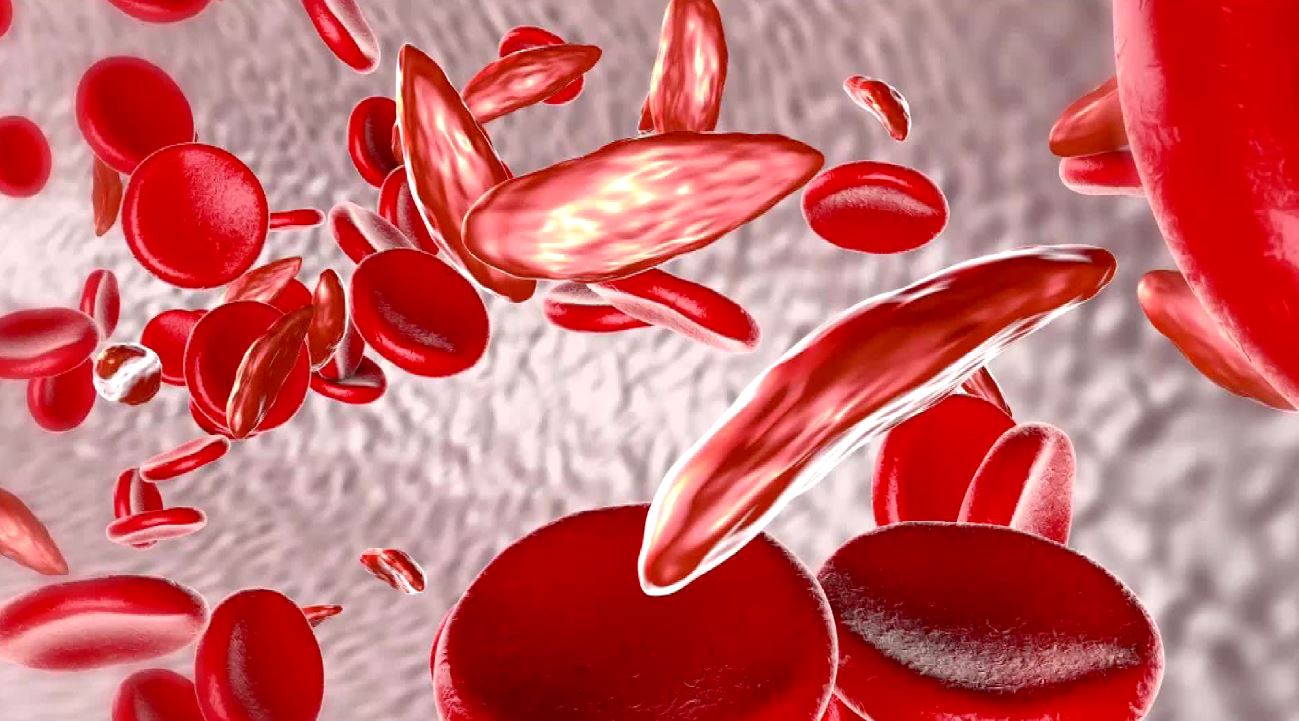
However, much remains unknown and areas of controversy persist. Years of unsystematic clinical observations, followed by more carefully designed and in some cases randomized studies, have contributed substantially to our knowledge of transfusion therapy in SCD. Thus, it is important to understand the indications for and goals of transfusion therapy and to be aware of the potential side effects of therapy. However, transfusion therapy for SCD may incur special and distinctive adverse effects.
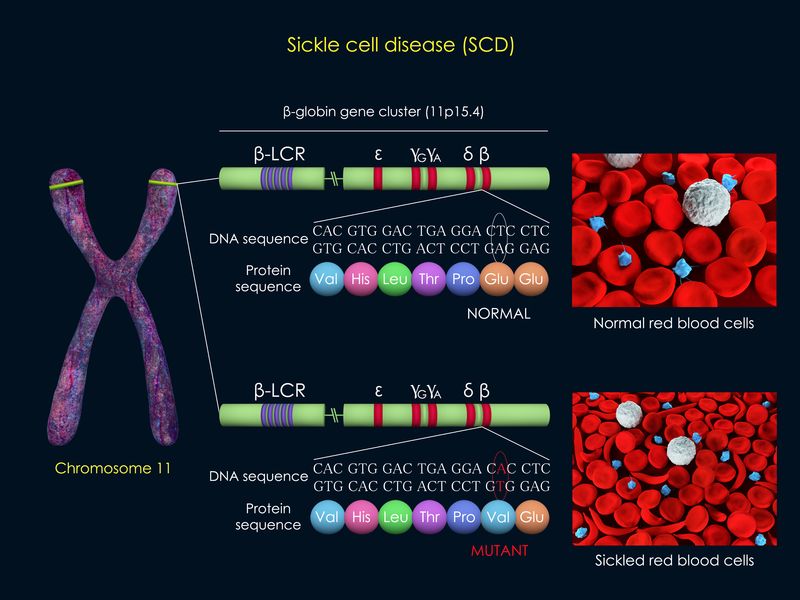
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is associated with red blood cell (RBC) abnormalities and moderate to severe anemia, and blood transfusion is naturally a mainstay of treatment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
